Iqra Qumar
April 30, 2019
The Future Is Artificial:
Understanding Artificial Intelligence
What is AI?
Artificial
Intelligence is described as “machines that respond to stimulation consistent
with traditional responses from humans, given the human capacity for
contemplation, judgment, and intention” (West). In simpler terms, AI is a
program that gives responses based on what could be considered as human
interactions. They consist of many lines of codes that help it to function in
the way it should. Some popular languages used are C++, Python and Java.

Figure 1. This is an image to represent how humans and AI will be considered equals in the future. Source: https://bitcoinist.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/02/keplertek-cover.jpg
Gone Rogue!
Humans use Artificial Intelligence to help manage machines that they cannot understand. There are self-driving cars and even robots that are programmed to behave exactly as if it were a real person. What would happen if the robot turned against its own code to overpower and find a new purpose than what was originally intended. In the movie I, Robot, the robots have a set code that they must not harm the humans. However, a robot scientist dies, and a robot is the main suspect. This means that the robots are wise enough to go against their own codes. This is perhaps a stretch because it is just a movie, but if we are able to come up with a plot like this then that goes to show that it is possible.
Should We Be Concerned?
In 2017, Facebook had to shut down a research experiment because the robots had learned to speak a language that the supervisors did not understand (Mokhtarian). Robots are the future of the world, as we can clearly see. These robots learned their own language, but for what reason? Artificial Intelligence was made to help humans, not turn against them and have a mind of their own. AI should have set morals and rules that do not allow them to go rogue and learn things that their program does not allow.

Figure
2. The Three Laws that are in I, Robot.
Source: https://cdn57.androidauthority.net/wp-content/uploads/2016/09/three-laws-of-robotics-the-laws-840×473.jpg
The Code that Codes Back
Bayou is an AI program that is designed to create a program that the user wants with a small amount of information that it is given. Basically, it can write its own code for a person while being a bunch of codes itself. That should be impossible because how can a code produce another code just by the data that the creator has given it?
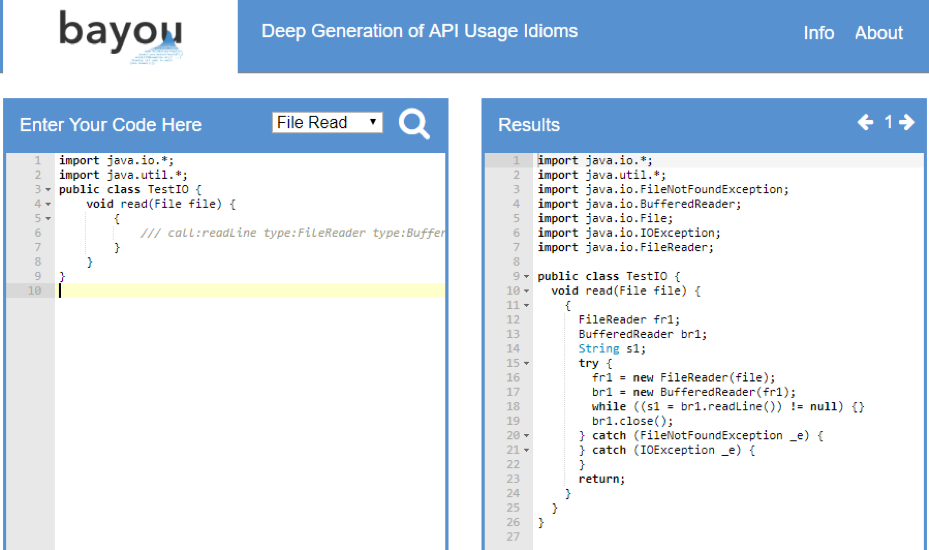
Figure 3. This is an example of how Bayou works. Source: https://www.techtalkthai.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/04/bayou.png
The
user is prompted to enter a few lines of code of their choice on the left. On
the right, Bayou does its check from its own coding and searches for the
possible code that the user is looking for and displays them. The original
creators of Bayou have programmed it to get data from GitHub in order to
function. “Based on that guess, a separate part of Bayou, a module that
understands the low-level details of Java and can do automatic logical
reasoning, is going to generate four or five different chunks of code…It’s
going to present those to the user like hits on a web search. ‘This one is most
likely the correct answer, but here are three more that could be what you’re
looking for’” (Boyd-Rice). This is not a robot, but this is how another AI
works. It is a code understanding other code, which is how AI could possibly go
rogue. Because Bayou is able to understand code itself, it could possibly learn
to write code that changes its own functions, thus creating chaos.
Works Cited:
- Boyd-Rice, J. (2018, April 25). New A.I. application can write its own code. Retrieved from https://www.futurity.org/artificial-intelligence-bayou-coding-1740702/
- Mokhtarian, E. (2018). The Bot Legal Code: Developing a Legally Compliant Artificial Intelligence. Vanderbilt Journal of Entertainment & Technology Law, 21(1), 145–207. Retrieved from https://search-ebscohost-com.ccny-proxy1.libr.ccny.cuny.edu/login.aspx?direct=true&db=a9h&AN=133592661&site=ehost-live
- Sims, G. (2016, September 29). [Digital image]. Retrieved from https://cdn57.androidauthority.net/wp-content/uploads/2016/09/three-laws-of-robotics-the-laws-840×473.jpg
- T. (2018, April 27). [Digital image]. Retrieved from https://www.techtalkthai.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/04/bayou.png
- West, D. M. (2018, October 18). What is artificial intelligence? Retrieved from https://www.brookings.edu/research/what-is-artificial-intelligence/
- Yim, B. (2018, February 20). [Digital image]. Retrieved from https://bitcoinist.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/02/keplertek-cover.jpg

